Imagine you’re building your dream home. You have your design prepared together with your team, but when inspecting blueprints, they seem difficult to understand. It takes time to understand the meaning of the initial inspection of all line symbols and numerical values.
Unless you know what you’re reading, mistakes can easily be made. A misread measurement or an off-key door can lead to delays, cost additional money, and cause stress later on.
But the best part? Reading blueprints isn’t as difficult as it appears.
This guide will simplify all the basic components of blueprints so you can understand their lines and symbols. After completing it, you will feel comfortable reading your blueprints and maintaining project progress.
What Are Construction Blueprints?
Construction blueprints, or plans, are detailed drawings that indicate how a building will be constructed. They contain measurements, materials, and specifications, instructing all from architects to contractors.
Blueprints show the building’s design and where the doors, windows, and plumbing will be. They help ensure everything is constructed correctly and as intended.
The word “blueprint” originated from a former method of printing that produced white lines on blue paper. Blueprints are now usually printed on white paper in black and white or color.
A study from the Construction Management Association of America demonstrates that errors in blueprints result in as much as 30% of all construction rework. People need to fully comprehend construction blueprints to prevent expensive errors and save money and time on construction activities.
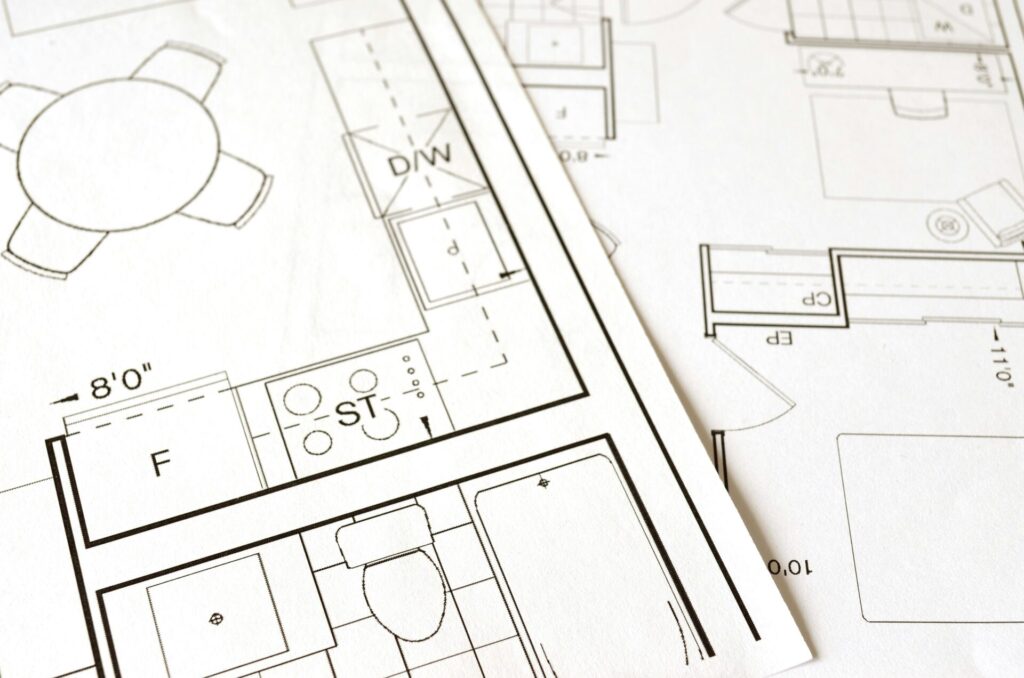
The Importance of Blueprints in Residential Construction
Blueprints are more than just drawings—they help guide the whole building process.
They Keep the Project on Track
Blueprints show what needs to be done and how to do it. When everyone follows the same plan, confusion, delays, and costly mistakes are avoided.
They Help You Follow Rules and Stay Safe
Every home must meet local building codes and safety rules. Blueprints show that your design follows these rules before construction begins. This helps avoid fines or having to fix things later.
They Save Time and Money
The use of good blueprints produces effective future planning tools. Blueprints enable you to calculate necessary materials as well as establish financial limits and timetable development. The early detection of issues through blueprints saves costs because problems can be rectified before spending more money on fixes.
A 2021 study by the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) found that 72% of home builders said clear blueprints helped them avoid expensive mistakes and stay on schedule.
Key Features of a Blueprint
A blueprint includes multiple components and parts that work together to produce precise plans with clear details. Understanding these key features is the first step in learning how to read blueprints.
| Feature | Description |
| Title Block | Provides key project details like the project name, location, architect/contractor info, and date of the blueprint. |
| Revision Block | Tracks any changes made to the blueprint to ensure all parties are using the latest version. |
| Grid System | Divides the blueprint into sections for easy reference, helping contractors quickly locate specific areas of the plan. |
| Notes and Legends | Explains symbols and abbreviations used on the blueprint, ensuring accurate interpretation of the drawing. |
| Drawing or Plan | The main part of the blueprint shows the layout, dimensions, and important features of the construction project. |
In a survey conducted by the Construction Industry Institute, 64% of project managers said that clear blueprint details directly correlated with successful project delivery on time and within budget.
Types of Blueprints in Residential Construction
Residential construction blueprints are divided into multiple types, which examine different project components. The main blueprint categories include:

Architectural Blueprints
These Blueprints show the entire building structure through floor plans, elevations, and sectional views.
Structural Blueprints:
The structural blueprint contains drawings that show all components including foundations, along with beams and necessary load-bearing walls.
MEP Blueprints (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing)
In MEP Blueprints (Mechanical Electrical Plumbing), users can find specifics for mechanical systems (HVAC), electrical systems (wiring and outlets), and plumbing systems (pipes and drains).
Landscape Blueprints
Landscape Blueprints focus on outside property elements, including gardens alongside driveways, lawns, and patios.
Civil Blueprints
The civil blueprints present site plans for drainage, grading, and utilities, which harmonize the house with its surrounding environment.
| Did You Know? MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) systems cost approximately 20% of the overall construction cost, highlighting the significance of precise MEP blueprints in preventing expensive errors. |
Types of Sheets in a Blueprint Set
Here’s a simplified and easy-to-read table for the Types of Sheets in a Blueprint Set for residential construction:
| Sheet Type | Description |
| G Sheets | General sheets with project details, site plans, and notes. |
| A Sheets | Architectural plans showing floor layouts, elevations, and building sections. |
| S Sheets | Structural plans that cover foundations, beams, and load-bearing structures. |
| M Sheets | Mechanical plans showing HVAC systems (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning). |
| E Sheets | Electrical plans with layouts for outlets, lighting, and wiring. |
| P Sheets | Plumbing plans with water lines, waste pipes, and fixtures. |
| L Sheets | Landscape plans for yards, gardens, and outdoor features. |
Common Perspectives in Blueprints
Multiple blueprint views are drawn from different angles to deliver a comprehensive understanding of the construction process. The following explanation covers the fundamental blueprint views:
- Plan Views: The most prevalent blueprint view shows the foundation layout by presenting an aerial view of rooms and their associated doors and windows.
- Elevation Views: The side view presentation of the building provides information about its vertical dimension and external characteristics.
- Cross-Section Views: Cross-Section Views show the building’s interior by cutting through it and displaying elements such as walls, floors, and roofs.
- Isometric Views: Shows the building in three dimensions, thereby demonstrating better spatial relationships among various areas.
According to AIA research, residential blueprint sets contain plan views in 70% of their overall sheets, and elevation views make up the remaining 20%.
How to Read Construction Blueprints
The following section instructs you on how to understand blueprint components after clarifying their major structural features.
- Start with the Title Block: This initial section contains vital project information concerning revisions within the Title Block. Make sure you verify the blueprint version, as it contains the most up-to-date information.
- Review the Dimensions: Use the defined measurements to study the actual dimensions because blueprints reflect scaled drawings of rooms and their components.
- Learn the Symbols: Make sure to learn both symbols and abbreviations that frequently appear in blueprints. Sometimes, these symbols can be discovered in the blueprint’s legend section.
- Check the Views: Read the initial views as well as their subsequent sections to grasp both the building layout alongside its construction information.
- Read the Notes: Examine the Notes and Legends because they contain extra explanations related to particular construction elements.
The National Research Council conducted a study that shows that blueprint misinterpretation resulting from incorrect reading leads to 30% of all construction delays.
Blueprint Symbols and Abbreviations
The standard symbols, along with abbreviations located within blueprints, serve to show different building components. The symbols exist to eliminate space waste and simplify the transfer of information. For example:
- D might represent a door.
- W could stand for a window.
- L might represent light fixtures.
Check the legend section of the blueprint to decode its symbols and abbreviations.
8 Types of Blueprint Lines and What They Mean
Blueprints use different types of lines to convey various aspects of the design. Here’s what each line means:
| Line Type | Description |
| Object Lines | Show the visible edges or outlines of objects. |
| Hidden Lines | Represent parts that are not visible from the current view (behind other items). |
| Dimension Lines | Indicate the size or distance between two points, like room or wall length. |
| Center Lines | Mark the center of symmetrical parts, such as doors, windows, or circles. |
| Phantom Lines | Show alternate or future positions of an object (e.g., moving parts). |
| Extension Lines | Extend from the object to show where the dimension starts and ends. |
| Leader Lines | Link notes or labels to specific features in the drawing. |
| Break Lines | Indicate that a part of the drawing is not shown to save space or focus detail. |
Why Blueprint Reading Matters in Residential Construction
Proficiency in blueprint interpretation forms an essential requirement among all professionals who work on residential buildings. Here’s why it’s so important:
- Ensures Accuracy: The detailed blueprint information enables accurate work which reduces the likelihood of making costly mistakes.
- Helps Meet Codes: Accurate blueprints protect builders from legal issues because they meet all regional building standards and zoning requirements.
- Improves Communication: The blueprint reading strengthens the foundation for contractors to collaborate efficiently by sharing essential information with engineers and architects.
Tips and Tricks for Blueprint Reading
Here are some tips you can use while reading the blueprint for residential construction.
- Keep a Symbol Guide Handy: Print a legend of common abbreviations and symbols.
- Use Colored Pencils: Highlight electrical, plumbing, and structural elements in different colors.
- Walk the Site: Compare the blueprint to the physical space during inspections.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Blueprint Reading
- Skipping the Title Block: Always check the blueprint version stated in the title block because using out-of-date drawings will lead to confusion.
- Overlooking Symbols: Before interpreting blueprints, check the legend for its symbols and abbreviations since they protect against misreading information
- Ignoring Dimensions: Pay attention to the scale and dimensions to prevent mistakes in construction.
FAQs
Does anyone need engineering knowledge to understand blueprint drawings?
Yes! Reading blueprints requires time, but anyone who devotes practice and perseverance will achieve understanding in this skill.
How does the scale measurement appear on blueprint drawings?
The blueprint drawing attaches to actual dimensions through its scale representation. The blueprint shows 1/4″ corresponds to actual measurements of 1 foot.
How do blueprints help prevent mistakes?
Blueprints provide clear instructions, which helps avoid errors during construction. Misreading them can lead to up to 30% of project rework.
How do I read measurements on a blueprint?
Measurements are shown with lines and numbers. The numbers tell you the size, and the lines connect them to the design. Always check the scale to understand the real size.
Is it possible to modify the blueprint after starting construction?
A blueprint can accept minor modifications, provided proper examinations happen before the blueprint receives updates. Both design modifications must receive approval for implementation.
Conclusion
Understanding blueprints requires initial practice combined with proper methods, which makes the process more manageable. Reviewing the blueprint features together with their symbols and lines enables better interpretation of blueprint plans, which ensures successful construction projects.
Ready to get started? If you’re planning a construction project and want to make sure your blueprints are accurate and easy to understand, contact us at Prime Estimation. We’ll help you understand the details and avoid costly mistakes. Let’s keep your project on track!











